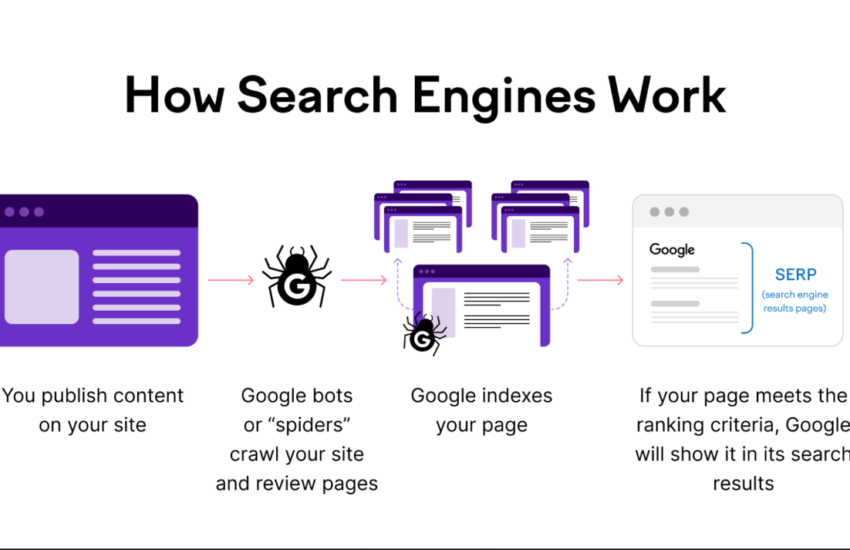
Indexes are the backbone of search engines. If your content isn’t indexed, it can’t show up in Google search results — no matter how valuable it is. But how do you know Google indexed your content correctly — especially long or detailed pages? Below is a clear, up-to-date guide covering what indexing is, how to verify it, and advanced checking methods.
📌 What Indexing Really Means
Before we jump into techniques, let’s define indexing:
Indexing is the process where Google’s bots:
- Crawl your page (discover it),
- Render/Analyze the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and
- Add it to Google’s index so it can show in search results.
If a page isn’t indexed, Google won’t rank it — no matter how good the content is.
🔍 1. Check Indexing Using Search Operators (Quick Test)
The easiest first step — no tools required.
site:YOURURL
In Google Search, type:
site:yourwebsite.com/your-page-slug
If the page appears, it’s indexed. If nothing shows up, Google doesn’t currently include it in its index.
Tip: This is fast but not always precise — particularly for longer pages with many sections.
🛠 2. Use Google Search Console — Most Reliable Method
Google’s own tools give the best answers.
URL Inspection Tool
- Open Google Search Console and pick your property.
- Go to URL Inspection.
- Paste the full page URL.
- See the result:
- URL is on Google → indexed.
- URL isn’t on Google → not indexed.
This shows exactly how Google last viewed your page and whether the HTML was accepted into the index.
📊 3. Page Indexing Report (Bulk Overview)
If you want to check many pages at once:
- In Search Console go to Indexing > Pages.
- You’ll see:
- Indexed pages
- Pages not indexed
- Reasons why they aren’t indexed (e.g., noindex tags, crawl errors)
This is great for site-wide index health.
📖 4. Confirm Specific Content Passages
So what about long documents where you worry parts might not be indexed?
Google expert John Mueller recommends an easy trick:
🔎 Search for a distinct passage from deeper down the page (in quotes).
Example:
"this unique sentence from the middle of your article"
If this search result appears, then that part of the content is indexed and available to rank. It’s a simple and effective test to confirm indexing of specific content, not just the URL.
🧠 Why Some Pages Don’t Get Indexed
Even when crawled, Google may leave a page out of the index if:
- It’s marked noindex,
- It lacks internal links, or
- The content is low-value or duplicated.
Fix technical issues first (robots.txt, sitemap, meta tags) before asking Google to index again.
✔️ Best Practices to Boost Indexing Chances
✅ Submit your sitemap in Search Console
✅ Use internal links to important pages
✅ Ensure content is unique and valuable
✅ Use structured data where relevant
✅ Fix crawl issues reported in Search Console
These improve not only indexing, but ranking potential too.
📌 Final Thoughts
Indexing is the foundation of SEO. Knowing whether your entire document — especially long or complex pages — is indexed helps you avoid wasted effort and capture traffic you deserve.
Use Search Console first, then validate content sections with search quotes to double-check deep passages. Once you confirm indexing, you’re ready to optimize performance and visibility.